A Guide to 3D Motion graphics: End-to-End Studio Production
Imagine the difference between a flat architectural blueprint and a dynamic, 3D model you can actually walk through. That leap from flat to immersive is exactly what 3d motion graphics brings to the table. It’s the art of breathing life into graphic elements, text, logos, shapes, by animating them in a three-dimensional space to create genuine depth, realism, and impact.
Defining the Dimensions of Motion
At its core, 3d motion graphics is all about breaking free from the two-dimensional world. Instead of just moving left, right, up, and down (on the X and Y axes), we add a third dimension: depth (the Z-axis). This one addition is a game-changer, turning flat designs into tangible objects you feel you can see from any angle. The process is a lot like digital sculpting. Take a product visualisation, for example. You’re not just drawing a picture; you're building an object from the ground up, giving it a specific texture, and placing it under virtual lights to see how shadows naturally fall across its surface.
The Core Artistic Tools
Getting from a flat concept to a dynamic 3D asset happens in a few key stages. These aren't just technical terms; they're the fundamental building blocks artists use to craft compelling visual experiences.
- •Modelling: This is the sculpting phase. Here, an artist builds the object's shape and structure, almost like creating a wireframe skeleton for a character or the chassis for a car.
- •Texturing: With the model built, it's time to give it a surface. Texturing is where a plain grey sphere becomes a realistic football, complete with the grain of the leather, or a logo gets that shiny, metallic finish.
- •Lighting & Rendering: This final step is essentially a virtual photoshoot. Artists position digital lights to create mood, depth, and believable shadows. Rendering is the heavy lifting, where the computer calculates all that information, light, textures, shadows, and movement, to generate the final, polished frames of the animation.
For anyone in marketing or brand management, getting your head around these elements is key. It’s not about knowing the software, but about understanding how depth, light, and texture can make a product showcase pop, simplify complex data, or build a truly memorable brand identity.
From Simple Shapes to Complex Worlds
The real power of 3d motion graphics is its sheer scalability. It can be as straightforward as making a company logo spin in 3D space with realistic reflections, creating an elegant and professional brand sting. But at the other end of the spectrum, it can be used to construct entire virtual worlds for a TV show's title sequence or build immersive training simulations. Ultimately, it’s a powerful toolkit for communication. It lets you show how a complex machine works from the inside out, visualise data in a way that feels intuitive, or simply make a brand message feel more solid and significant. It closes the gap between an idea and reality, turning abstract concepts into visuals you can almost reach out and touch.
The Production Journey: From Brief to Final Render
Creating great 3d motion graphics isn't a quick sprint; it's a well-planned expedition from pitch to delivery. It’s a structured, collaborative process that carefully transforms a spark of an idea into a polished, final piece. Understanding this workflow demystifies what we do, making sure everyone is on the same page at every key moment, from the first scoping call to the final handover. The whole thing kicks off not with software, but with a conversation. A solid creative brief is the map for the entire project, clearly laying out the goals, audience, key messages, and the desired visual style. From there, our creative team gets to work on concepts, scripts, and storyboards , a visual blueprint that maps out the animation's flow, shot by shot. Getting this stage right is vital for setting the story and visual direction before any heavy lifting in 3D begins, saving a huge amount of time and money later on.
Building the Digital World
Once the storyboard gets the green light, we move into the core 3D production phase. This is where the digital world is built from scratch, piece by piece, following a sequence designed for quality and efficiency.
- Modelling: This is the starting block. Artists build the 3D shapes of every object and character, essentially creating the digital "sculptures" that will fill the scene. Whether it’s a new product or a sprawling environment, this is where it first takes form.
- Texturing and Shading: With the models built, it's time to give them a surface. We apply textures, colours, and materials, think brushed metal, rough concrete, or gleaming glass, to make everything look and feel real.
- Rigging: For anything that needs to move in a complex way (especially characters), a digital "skeleton," or rig, is created. This rig is what allows our animators to manipulate the model and bring it to life with natural, fluid movements.
Bringing the Scene to Life
With all the digital assets prepped and ready, the animation can finally begin. This previz (pre-visualisation) stage involves moving the objects, characters, and virtual cameras, following the blueprint laid out in the storyboard. It’s a detailed process where timing, pacing, and performance are all fine-tuned to tell the story effectively and create the right emotional impact. After animation comes lighting. We strategically place digital lights to craft the mood, highlight key details, and produce realistic shadows and reflections. This stage has a massive influence on the final look and feel, turning a collection of animated objects into a cohesive, atmospheric world. A crucial stage in this journey is understanding what is video rendering, the technical process that pulls every creative element together into a final video file. This is the last, and most computer-intensive, step where the software calculates every single frame, combining all the models, textures, lighting, and animation into the finished high-resolution images. This chart breaks down the core stages of creating 3D graphics, from the initial build to the final output. As you can see, each step logically builds on the one before it, which keeps the workflow structured and predictable.
As you can see, each step logically builds on the one before it, which keeps the workflow structured and predictable. The Final Polish
The last leg of the journey is compositing and post-production. Here, all the rendered frames are assembled, and the final touches are applied. This might include colour grading to perfect the visual tone, adding special effects like smoke or lens flares, integrating 2D graphic elements, and syncing everything up with the final sound design and music.Every step in this journey includes critical client touchpoints. Feedback on storyboards, previz, and lighting tests ensures the project stays on track and aligns perfectly with the initial vision, resulting in a final product that meets, and exceeds, expectations.
The Tech Behind Today’s Motion Graphics
To create the jaw-dropping visuals we see on screen, artists and studios lean on a powerful set of specialised tools. Think of it as a digital workshop, where raw ideas are modelled, animated, and brought to life. Getting to grips with these core technologies helps demystify how different creative results are achieved, from hyper-realistic product animations to interactive virtual worlds. At the heart of most 3d motion graphics projects, you’ll find dedicated modelling and animation software. This is where artists get hands-on, building, texturing, and animating every single asset from scratch.The Cornerstones of 3D Creation
Industry workhorses like Cinema 4D and Blender are staples in almost every production pipeline. Cinema 4D is widely loved for its intuitive interface and powerful MoGraph toolset, which makes it a go-to for complex abstract animations and slick broadcast graphics. Blender, on the other hand, is a hugely capable open-source powerhouse that can handle an entire project from start to finish, from initial sculpting right through to the final video edit. For a deeper dive, check out our guide on the best 3D animation software of 2024. These platforms are the bedrock for:- •Detailed Asset Creation: Building everything from intricate character models to pixel-perfect architectural visualisations.
- •Keyframe Animation: Carefully setting key poses for an object or character and letting the software create the smooth motion in between.
- •Photorealistic Texturing: Applying digital materials that convincingly mimic real-world surfaces, like brushed metal or polished wood.
This traditional approach produces stunning, high-fidelity results, but it has one major catch: rendering time. It often takes computers hours, or even days, to painstakingly calculate all the light, shadows, and reflections for the final frames.
Real-Time Engines: The New Frontier
Lately, a massive shift has been happening, driven by technology straight out of the video game industry. Real-time engines like Unreal Engine and Unity are completely changing the game. Instead of pre-rendering every single frame, these engines generate high-quality images instantly. This unlocks the door to interactive experiences and radically faster production timelines.
Think of it like the difference between a photograph and a live video feed. Traditional rendering gives you a perfect, static image, while a real-time engine provides a dynamic view that you can change and interact with on the fly.
This isn't just about working faster; it's about working smarter and more creatively. Clients can now review animated scenes live, asking for tweaks to lighting or camera angles and seeing the changes happen immediately. This is the technology powering everything from VR training simulations and AR mobile apps to interactive product configurators. The numbers back it up. The UK 3D rendering market, a close cousin of 3d motion graphics, generated $254.9 million in revenue and is projected to hit a staggering $1,145.2 million by 2033. Engines like Unity and Unreal are huge drivers of this growth, something Studio Liddell has been tapping into for our animation and XR projects since 1996. You can explore more about these market trends and their drivers. Producers and clients often ask which engine is the right fit. While both are incredibly powerful, they have distinct strengths that make them better suited for different kinds of projects.
Choosing the Right Engine for Your Project
| Feature | Unreal Engine | Unity Engine | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|
| Visual Fidelity | World-class, photorealistic rendering out-of-the-box with tools like Lumen & Nanite. | Highly capable, but often requires more setup and assets to achieve photorealism. | Unreal: High-end architectural visualisation, automotive commercials, virtual production, console games. |
| Ease of Use | Blueprint visual scripting is great for artists, but the engine can be complex. | Generally considered more user-friendly and easier for beginners to pick up. | Unity: Mobile games, AR/VR applications, interactive 2D/3D experiences, rapid prototyping. |
| Asset Store | Growing library of high-quality assets. | Massive, mature marketplace with a huge variety of assets for any budget. | Both: Strong ecosystems for sourcing pre-made models, textures, and tools to speed up development. |
| Platform Support | Excellent support for high-end PCs, consoles, and VR. | Unmatched support for a vast range of platforms, especially mobile (iOS/Android). | Unity: Projects targeting a wide array of devices, particularly mobile-first applications. |
Ultimately, the choice depends on your project's specific goals, whether you're aiming for breathtaking realism for a film or broad accessibility for a mobile AR app.
The Rise of AI and Procedural Tools
Beyond the big engines, a new wave of AI and procedural tools is making workflows even more efficient. AI tools can now automate tedious tasks like rotoscoping (cutting objects out of video) or even generate endless texture variations, which frees up artists to spend more time on creative problem-solving. Procedural tools, like those found in Houdini, let artists build complex visual systems using rules and algorithms. This is the secret sauce for generating natural phenomena like swirling smoke, flowing water, or massive crowds without having to animate every single element by hand. These technologies all work together. By combining the precision of traditional 3D software, the speed of real-time engines, and the smarts of AI, modern studios have an incredible amount of flexibility. We can now deliver higher quality work, on tighter deadlines, and with more creative freedom than ever before.
How 3d Motion Graphics Drive Business Results

It’s one thing to understand the tech, but it’s another to see how it actually affects the bottom line. 3d motion graphics aren’t just about pretty pictures; they are a serious business tool. Across countless industries, they’re being used to solve real challenges, grab audience attention, and deliver results you can actually measure. Whether it’s stopping the endless scroll on a social media feed or breaking down a ridiculously complex technical idea, the applications are as diverse as they are effective. The real strength of this medium is just how flexible it is. You can mould it to fit almost any strategic goal, be it cranking up brand awareness, driving sales, or making training materials stick. By adding a sense of depth and realism to visual stories, brands can get their message across with way more clarity and punch than with a static image or standard video.
Applications in Marketing and Advertising
In the ridiculously crowded world of digital marketing, just getting noticed is half the battle. This is where 3d motion graphics give brands a real advantage, letting them show off products and services in ways that are just impossible with a camera or 2D animation.
- •Dynamic Product Visualisations: Imagine letting your customers spin a new product around, see every single angle, watch it assemble itself, or even peek inside to see the mechanics. That level of detail builds a huge amount of trust and desire, which translates directly into better engagement and higher conversion rates.
- •Captivating TV Commercials: From photorealistic splashes of liquid for a drink advert to bringing a whimsical character to life for a brand campaign, 3d motion graphics take TV ads to another level. They create those memorable spots that actually stick in your head long after the ad break is over.
- •Engaging Brand Storytelling: A slick animated logo, a cinematic title sequence, or a sharp explainer video can tell your brand's story in seconds. We've put together some great examples in our guide to motion graphics services for brands.
The demand for this kind of work is exploding. To give you an idea, the UK 3D rendering services market, a core part of this industry, shot up from $955 million in 2017 and is on track to hit nearly $7 billion by 2025. This isn’t just a blip; it shows how the UK is cementing its place as a powerhouse in digital creative production.
Impact on Entertainment and Media
It’s not just about selling things. 3D motion graphics are the absolute bedrock of modern entertainment. They are essential for building the immersive worlds and telling the compelling stories we’ve all come to expect from films, TV, and gaming. Think about the cinematic title sequences for big TV shows or films. They use 3d motion graphics to set the entire tone and pull you into the world before a single line of dialogue is spoken. They're also vital for creating stunning visual effects, entire animated series, and the richly detailed environments you see in video games. It’s what gives high-end productions their visual polish.
Advancing Corporate Training and Education
This might be one of its most powerful uses. When you need to explain something that's too complex, dangerous, or just plain expensive to show in real life, 3d motion graphics are the perfect answer.
By creating clear, accurate, and engaging visualisations, businesses can simplify intricate processes, making them easier for employees and stakeholders to understand. This leads directly to better knowledge retention and improved performance.
Just look at these use cases:
- •Technical Explainers: A 3D animation can take a complex piece of machinery apart, showing exactly how every component works together in perfect harmony. This is absolute gold for engineering, manufacturing, and technical sales teams.
- •Immersive VR Simulations: For high-stakes training, like surgical procedures or operating heavy machinery, VR simulations built with 3D graphics create a safe, repeatable space for people to practise and master their skills without any real-world risk.
- •Stakeholder Communication: Trying to get buy-in for a new architectural plan or a complex financial model? A 3D visualisation makes the data instantly digestible, helping you secure investment far more effectively than any PowerPoint slide ever could.
Bringing Digital Characters to Life
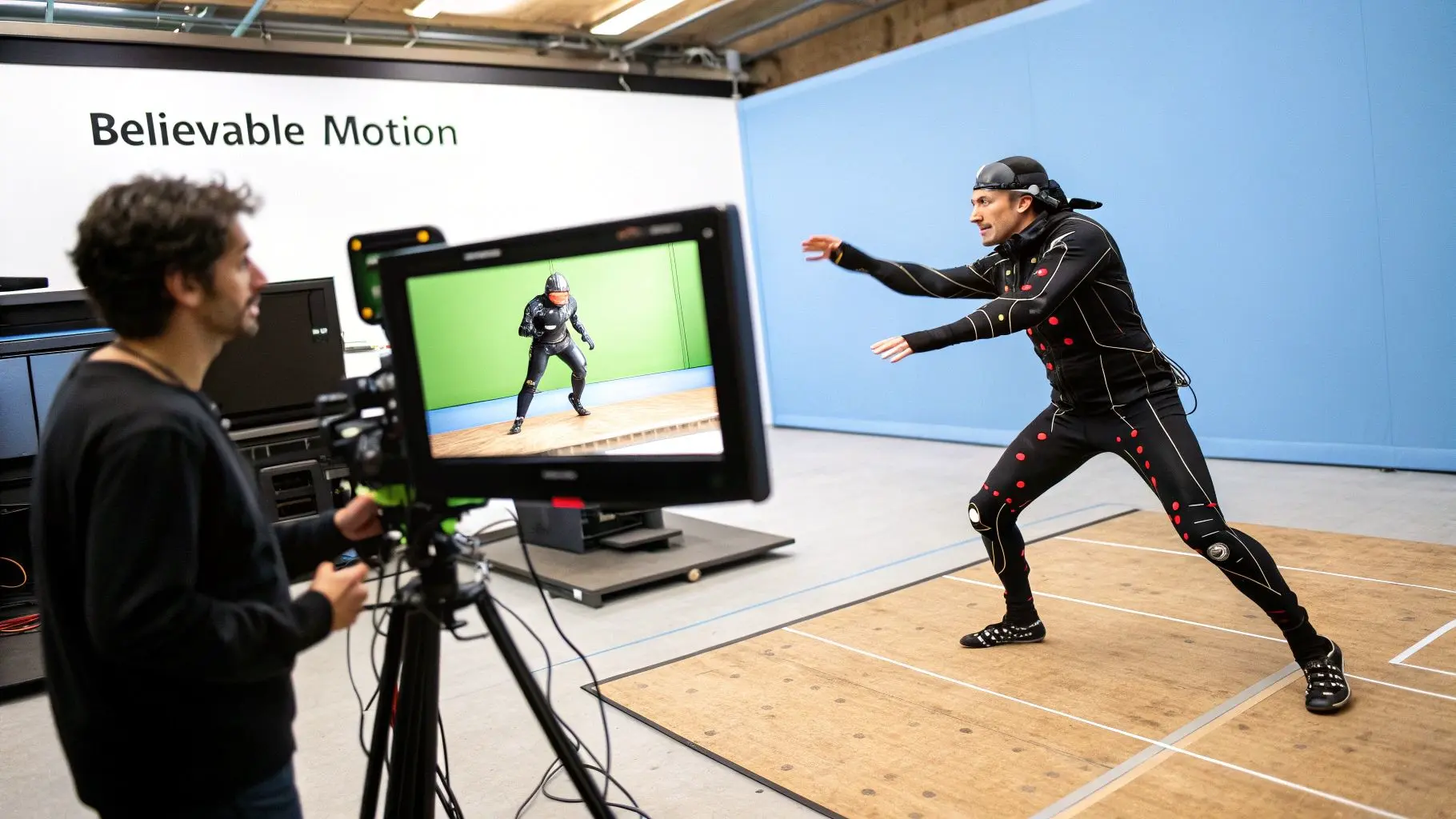

While slick logos and abstract shapes certainly have their place, the real soul of 3d motion graphics often emerges when we breathe life into characters. Getting a digital performance to connect with an audience on an emotional level is a delicate dance between raw artistic talent and sophisticated technology. It's here that animation techniques turn a static 3D model into a character that feels truly alive. The ultimate aim is always believability. It doesn't matter if it's for a Hollywood blockbuster, a kids' TV show, or a character in a VR world, the movement has to feel right. The industry generally relies on two core methods to achieve this, each with its own strengths that fit different creative visions and production realities.
The Power of Performance Capture
You’ve probably heard of motion capture, or "mocap." It’s a fascinating process where we record a real actor's movements and map that performance directly onto a digital character. By placing sensors all over the actor's body, we can capture every tiny gesture, every shift in weight, and all the little nuances that make a performance human. This data gives us an incredibly realistic foundation to build upon, making it the perfect choice for projects demanding authentic, lifelike movement. This approach is a game-changer for:
- •Realistic Humanoid Motion: Mocap is brilliant at capturing the natural flow of walking, running, and other organic movements that are a nightmare to animate perfectly by hand.
- •High-Volume Animation: When you need hours of animation for a video game or a long-running TV series, mocap can slash production time by capturing performances in real-time.
- •Subtle Character Acting: The tech picks up on all the small, almost unconscious tics and gestures that make an actor's performance feel genuine and heartfelt.
The UK animation scene has really embraced this technology. Fuelled by huge demand from the video game and film sectors, the use of motion capture shot up by 30% in 2023 alone. This is all part of the UK's booming motion picture industry, which is on course to pull in £8.1 billion in revenue by 2025.
The Artistry of Keyframe Animation
The other side of the coin is keyframe animation, a more traditional, hands-on craft. With this method, an animator manually sets crucial poses, the "keyframes", for a character at specific moments. The software then intelligently fills in the gaps, creating smooth motion between those key poses.
While mocap is all about capturing reality, keyframing is about creating it from scratch. This gives animators total artistic freedom to push and pull movements for stylistic effect, build fantastical creatures, or craft performances that gleefully ignore the laws of physics.
Keyframing is the go-to when a project calls for stylised action or movements that no human actor could ever perform. It's a true art form that requires a deep, intuitive understanding of weight, timing, and anatomy.
The Unseen Foundation: Rigging and Facial Animation
No matter which animation method you choose, none of it works without a solid technical foundation. Rigging is the crucial step of building a digital "skeleton" inside a 3D model. This skeleton, complete with joints and controls, is what allows an animator to bend, twist, and pose the character. A great rig is the difference between fluid, natural motion and a character that looks stiff and robotic. Facial animation is just as vital. So much emotion is conveyed through the tiny movements of our facial muscles. Complex facial rigs give animators control over everything from the slightest dart of the eyes to a a full-blown smile, bringing real personality to the performance. We've gone into more detail on this in our article on 10 hidden secrets to bring your 3D characters to life. Ultimately, the choice between mocap and keyframing boils down to what the project needs, it's a constant balancing act between the quest for realism, creative ambition, and the realities of the budget.
How to Choose the Right Motion Graphics Studio
Picking the right creative partner is a huge decision. It's the one that can truly make or break your project. Get it right, and you're not just buying a service; you're forming a strategic partnership that delivers fantastic results. But with so many studios out there, how do you find the perfect fit? It really boils down to three things: checking out their past work, understanding how they operate, and making sure they have the technical chops to bring your ideas to life. A studio's portfolio is your first, and most important, port of call. Don't just get wowed by the flashy visuals. Look deeper. Analyse the work for its stylistic range and technical quality. Do they consistently produce work that matches the vibe you're going for? Are their animations fluid, is the lighting believable, and are the compositions well-thought-out? A strong portfolio shows more than just talent, it shows versatility. This snapshot from our own portfolio gives you a feel for what we mean, showcasing everything from vibrant IP for kids to complex technical animations. The diversity you see here is a great indicator of a studio's ability to adapt its creative style to fit different brand voices and project goals.
Assessing Technical Expertise and Process
Once you've sized up the portfolio, it's time to look under the bonnet at a studio's production pipeline and tech skills. A transparent, collaborative process is always a good sign of an experienced team. They should be able to walk you through their workflow without any fuss, from the initial brief and storyboarding right through to final rendering and delivery. Make sure they highlight key milestones where you'll get to give feedback and sign off on progress. On top of that, ask about the tools they use. Are they comfortable with real-time engines like Unreal and Unity? This is especially important for interactive projects or jobs with tight deadlines, as these platforms offer a lot more flexibility and can seriously speed things up. A studio that invests in its tech stack is a studio committed to quality and efficiency.
Writing a Strong Creative Brief
Finally, a successful project really starts with you. A clear, detailed creative brief is the single most important document you can provide. Think of it as the North Star for the entire production, making sure everyone is on the same page from day one. Your brief should nail down these key areas:
- •Project Goals: What are you actually trying to achieve? Is it to drive sales, explain a tricky concept, or just build brand awareness? Be specific.
- •Target Audience: Who are you talking to? Pinpoint their demographics, what they're interested in, and what problems you're solving for them.
- •Key Messages: What are the one to three things you absolutely need the audience to remember after watching?
- •Tone and Style: How should it feel? Serious and corporate, or playful and energetic? It helps to share examples of other videos or designs you like.
- •Call to Action: What do you want the viewer to do next? Visit your site, book a demo, or follow you on social media?
When you take the time to properly vet potential partners and pull together a comprehensive brief, you're setting the stage for a smooth, collaborative, and successful project. This groundwork gives you the confidence to make an informed decision and find a studio that won't just execute your vision, but elevate it.
Your 3d Motion Graphics Questions Answered
When you're diving into the world of 3d motion graphics, a few practical questions always come up. Thinking about costs, timelines, and exactly what's what is completely normal. Getting these sorted from the start helps everyone get on the same page and makes the whole process run smoothly. Here are a few of the most common questions we get asked.
How Much Do 3D Motion Graphics Cost?
This is the big one, and the honest answer is: it really depends. The cost can swing wildly based on how complex, long, and stylised your project is. For a simple 15-second logo animation, you might be looking at a few thousand pounds. But for a detailed 60-second explainer video with custom characters and intricate environments, the budget can easily go from £10,000 to over £50,000. So, what moves the needle on price? A few key things:
- •Model Detail: How intricate do the 3D models need to be? Think simple geometric shapes versus a photorealistic car engine.
- •Animation Complexity: Are we talking about smooth camera pans or complex particle effects and fluid simulations?
- •Rendering Time: This is the final step where the computer crunches the numbers to create the finished frames. More complexity means more processing power and time.
The best way to get a solid number is to put together a clear brief. Once you have that, you can have a proper chat with a studio to get a quote that's actually tailored to your idea.
What Is the Difference Between 3D Motion Graphics and 3D Animation?
It's easy to see why these two get mixed up, but they really have different jobs to do. 3D animation is usually all about telling a story with characters, the kind of thing you'd see in a Pixar film or a TV series. It's driven by performance, emotion, and narrative. On the other hand, 3d motion graphics is about bringing graphic elements to life in a 3D space. We're talking about text, logos, data, and abstract shapes moving with depth and purpose. The goal here is usually to communicate an idea or create a specific mood. Think of it as graphic design with an extra dimension, perfect for title sequences, brand films, and visualising complex data.
How Long Does It Take to Produce a 3D Motion Graphics Video?
Just like cost, the timeline is tied directly to the scope of the project. A short and sweet logo animation could be wrapped up in just 2-3 weeks. A more standard 60 to 90-second explainer video usually takes somewhere between 6-10 weeks from the first conversation to the final file. That timeframe covers everything: writing the script, storyboarding, modelling, animating, getting your feedback, rendering, and adding sound design. Of course, bigger, more ambitious projects with photorealistic visuals can take several months. The key to keeping any project on track is a well-defined brief and clear, timely feedback.
Ready to turn your vision into a dynamic 3D experience? Studio Liddell has been creating studio-quality productions with broadcast pedigree since 1996. Book a production scoping call