How to Make Apps A Practical UK Guide
Every brilliant app starts life as a simple idea meant to fix a real problem. But transforming that spark into a commercial hit? That demands a serious reality check through proper validation. It’s all about digging deep into market research, nailing down the problem you're solving, and truly getting to grips with your target users. This is the groundwork that separates apps that soar from those that just… disappear.
Validating Your App Idea in the UK Market
Before you even think about writing a single line of code, the real heavy lifting begins. An idea, no matter how clever it seems in your head, has to be stress-tested against the cold, hard reality of the market. This stage isn't about your vision; it's about uncovering a genuine, pressing need that a specific group of people has. So many apps fail to get any traction after launch simply because they skipped this bit. Success really boils down to defining the problem you want to fix. The entire foundation of your app rests on clearly understanding what are problem statements are, which ensures you're actually solving something people care about. Ask yourself: is your app a "vitamin", a nice-to-have, or is it a "painkiller" that solves an urgent, frustrating problem? Both investors and users are always looking for painkillers.
Understanding Your Target Audience
Once the problem is clear, you need to know exactly who you're building this for. Vague demographic profiles just won't cut it. You need to create detailed user personas , essentially, semi-fictional characters based on real data that represent your ideal UK customer. A solid user persona should include:
- •Demographics: Age, location (think a London commuter vs. a student in Manchester), occupation, and income.
- •Behaviours: How do they use technology? What are their daily routines? What are their app habits?
- •Goals & Motivations: What are they ultimately trying to achieve that your app will help with?
- •Pain Points: What specific frustrations and challenges do they face that your app can wipe out?
For instance, a persona for a new budgeting app might be "Frugal Fiona," a 28-year-old marketing professional in Bristol who’s tearing her hair out trying to track her spending on lunches and sneaky subscriptions. This level of detail becomes your north star, guiding every single design and feature decision down the line.
Conducting UK-Specific Market Research
With your user personas sketched out, it’s time to get a feel for the UK market landscape. This is a two-pronged attack: talking to potential customers and sizing up your competition.
Never assume you know what users want. The whole point of research is to swap out risky assumptions for solid, validated knowledge. This is where you confirm that the problem you think exists is a problem people will actually pay to solve.
To get that direct feedback, try these methods:
- •Surveys and Questionnaires: Tools like Google Forms or SurveyMonkey are great for polling your target audience. Ask pointed questions about their specific pain points and what they're using now to solve them.
- •Interviews: Nothing beats a one-on-one chat with a potential user. This is where you’ll unearth the deeper, qualitative insights that surveys can never give you.
- •Focus Groups: Get a small group of people from your target demographic in a room (virtual or physical) to discuss your app idea. The live feedback is invaluable.
Analysing Your Competition
No app is an island. A thorough competitor analysis helps you see what's already working, spot glaring gaps in the market, and start shaping your own Unique Selling Proposition (USP). Dive into the UK App Store and Google Play and see who the top players are in your category. For each key competitor, break down their:
- •Features: What do they offer, and more importantly, what are they missing?
- •User Reviews: This is an absolute goldmine. What do their users love and, crucially, what do they hate?
- •Pricing Model: How are they making their money?
- •Marketing Strategy: How are they getting in front of UK users?
This analysis will help you carve out a unique space for your app. Even a simple initial build can lead to huge success if it solves a problem better than anyone else. To see how starting small and focused can be a powerful strategy, you can explore how a simple MVP app can make you millions. By validating your idea properly from the start, you're not just building an app; you're building a strong foundation for a successful business.
Choosing the Right Development Path for Your Project
So, you've validated your app idea. Fantastic. Now comes the really critical decision: what technology will you use to build it? This choice isn't just for the tech team; it has a massive impact on your budget, how quickly you can get to market, and what your final user experience will feel like. Picking between native, cross-platform, or even a specialised XR engine is one of the most important calls you'll make. Think of this as a strategic business decision, not just a technical one. A high-performance fintech app, for instance, that needs top-tier security and direct access to a phone’s hardware like biometrics? That's almost always going to be a native build. But a content-led app for a local retailer could launch far quicker and more affordably using a cross-platform approach, without users noticing any drop in quality.
Native vs Cross-Platform Development
Native development is the purist's approach. You build a completely separate app for each operating system, one for iOS (using Swift or Objective-C) and another for Android (using Kotlin or Java). The upside is unmatched performance, rock-solid reliability, and the ability to tap into every single feature the device offers. The downside? It requires maintaining two separate codebases, which means a bigger budget and a longer timeline. On the other hand, cross-platform development uses frameworks like React Native to write the code once and run it on both iOS and Android. This dramatically speeds things up and brings costs down, making it a brilliant choice for a huge number of apps.
At its core, the trade-off is performance versus efficiency. While cross-platform tools are incredibly sophisticated now, native will always have that slight edge in raw speed and getting access to the very newest OS features the moment they’re released.
In the UK, the market is split right down the middle, so reaching both iOS and Android users is essential. Android holds 50.1% of the market share, with iOS right behind at 49.3%. This near-perfect split is a big reason why cross-platform development has become so popular here. And the talent is here to back it up, there are 6,202 active UK mobile app developers on Google Play who have collectively built 25,229 apps, each averaging 394,870 downloads. It shows that homegrown expertise can absolutely compete on a global scale. This is where having a clear, validated idea becomes crucial before you even think about code.
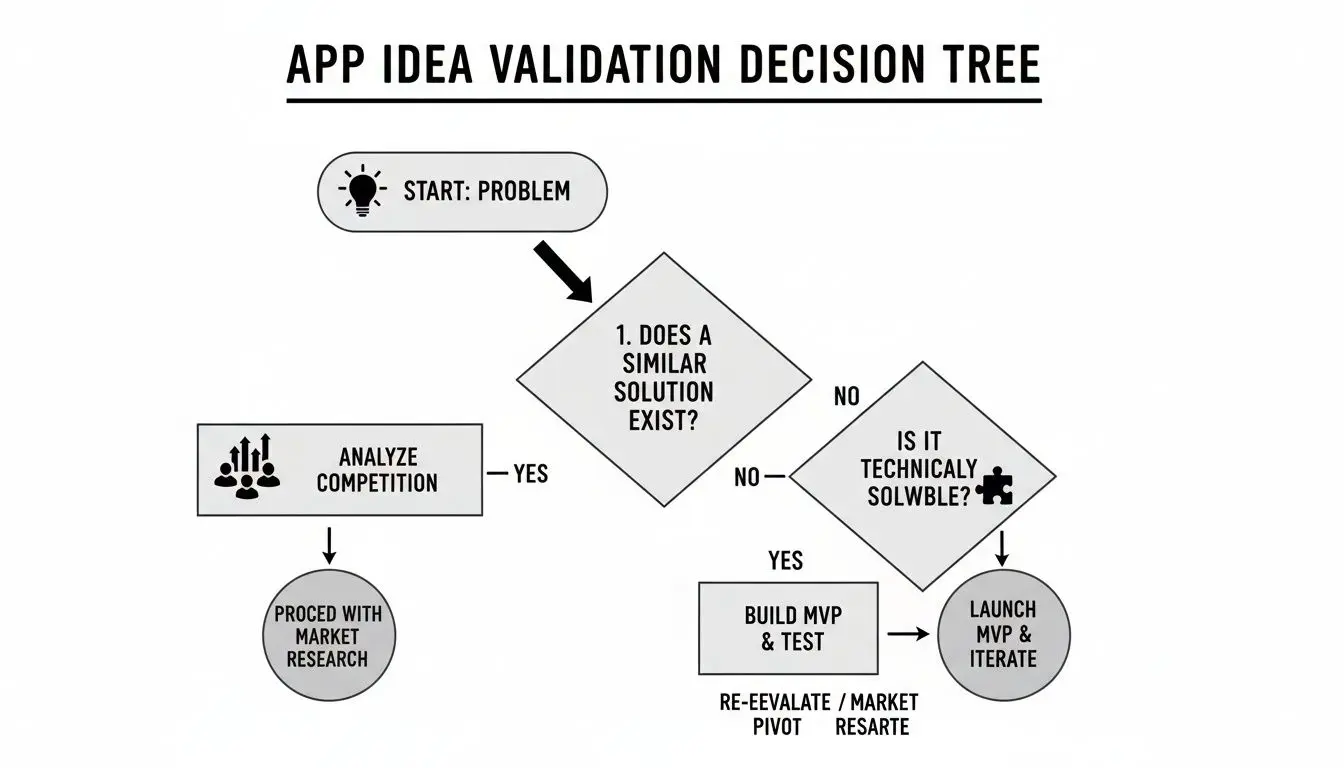
As the flowchart shows, everything starts with a real, solvable problem. Nail that first, and then you can confidently choose the right tools for the job.
App Development Approach Comparison
To help you weigh the options, here's a quick breakdown of the key differences between Native, Cross-Platform, and XR development.
| Factor | Native (iOS/Android) | XR (Unity/Unreal) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | Highest possible performance and speed. | Very good, but can have slight limitations for intensive tasks. | Optimised for high-fidelity 3D graphics and real-time rendering. |
| User Experience | Seamless, platform-specific UI/UX. | Consistent UI across platforms, but may lack native feel. | Highly immersive and interactive 3D/spatial experiences. |
| Cost | Highest, due to separate codebases and teams. | More cost-effective as code is shared. | Can be high due to specialised 3D artists and developers. |
| Time to Market | Slower, as two apps are built concurrently. | Faster, with a single codebase speeding up development. | Varies greatly based on complexity of the 3D world. |
| Hardware Access | Full access to all device features (camera, GPS, etc.). | Good access, but new features may have a delay. | Full access to specialised hardware (headsets, sensors). |
| Best For | High-performance, demanding apps (e.g., finance, complex games). | Content-driven apps, MVPs, most business applications. | Immersive training, AR retail, VR games, brand experiences. |
Ultimately, there's no single "best" answer. The right path is the one that best fits your specific project goals, budget, and timeline.
When to Consider Specialised XR Engines
Moving beyond the typical mobile app, we enter the world of eXtended Reality (XR), which covers both Virtual Reality (VR) and Augmented Reality (AR). For these truly immersive experiences, you need a different class of tool altogether: specialised game engines like Unity or Unreal Engine. These engines are the powerhouses for creating the interactive, 3D worlds that define XR. Think about the possibilities:
- •Retail: An AR app that lets a customer place a virtual sofa in their living room to see how it fits before they buy.
- •Training: A VR simulation that allows medical students to practise a tricky surgical procedure in a completely safe, repeatable environment.
- •Events: An immersive brand activation at an exhibition that stops people in their tracks and gives them a memorable, interactive moment.
The choice between Unity and Unreal often comes down to the project’s specific requirements, like the level of graphical detail needed and the existing skills of the development team. Building these experiences demands a very specific skillset, which is why many businesses choose to partner with a specialised studio. You can get a better sense of what's involved in our guide to app development services in the UK. As you map out your project, it’s also wise to consider all your resourcing options. Sometimes, looking further afield can be a smart move, and exploring a comprehensive guide to offshore app development can help you understand how to tap into global talent pools to manage costs and scale your team effectively. The best path is always the one that aligns your project’s ambition with the resources you have.
Designing an Experience Users Will Love
Now that you’ve picked your development path, it’s time for the real challenge: creating an app people actually want to use. A slick, intuitive design isn’t a nice-to-have anymore; it's the bare minimum for survival. Let’s be blunt: a clunky user experience is one of the main reasons apps get deleted just moments after being downloaded. This stage is make-or-break. The whole game boils down to two sides of the same coin: User Experience (UX) and User Interface (UI). Think of UX as the invisible architecture, the logic, the flow, how the app feels to navigate. UI is what you see and touch, the colours, the fonts, the buttons. For an app to succeed, they have to dance together perfectly.

This isn't just about aesthetics. Great design is a powerful business tool that directly drives user retention. UK consumers are already spending 4-5 hours a day glued to their phones, with over 75% of that time spent inside apps. To grab a slice of that attention, your app needs to be seamless, satisfying, even a little addictive. It’s a fiercely competitive space, but one where local knowledge gives you an edge. Just look at the 6,202 UK publishers on Google Play who average a massive 394,000 downloads per app, miles ahead of global averages. It shows that understanding your audience is key. You can dive deeper into mobile marketing insights and trends to see just how critical brilliant design really is.
From Wireframes to High-Fidelity Prototypes
You wouldn't start building a house without a blueprint, and you shouldn't build an app that way either. The design process is a journey, moving from rough sketches to a polished, interactive model, getting clearer and more detailed at every step.
- •Wireframing: This is the skeleton. Wireframes are super basic, low-fidelity layouts, often just black and white boxes. Their only job is to figure out the structure and where everything goes. You’re not worrying about colours or fonts yet, just pure function and flow.
- •Mockups: Once the blueprint is solid, you start painting the walls. Mockups are static, high-fidelity designs that show exactly what the app will look like. Here’s where you bring in the colour palette, typography, and branding to create a realistic snapshot of the final product.
- •Prototyping: This is where it all comes to life. Using tools like Figma or Adobe XD, designers link all the mockup screens together into a clickable, tappable simulation. This is your first chance to feel the user journey and iron out any navigational kinks before a single line of code gets written.
This iterative process, wireframe, mockup, prototype, is your best defence against costly development mistakes. It's far cheaper and faster to fix a design flaw in Figma than it is to rewrite code later on.
Core Principles of Great App Design
Every app has its own unique flavour, but the fundamentals of good design are universal. Nailing these will ensure your app isn't just functional, but genuinely a pleasure to use. #### Intuitive Navigation Your users should never feel lost. They shouldn't have to think about how to get from A to B. Keep your navigation simple, predictable, and consistent. For most mobile apps, this means sticking to familiar patterns, like a bottom tab bar for the main sections or a hamburger menu for everything else. The goal? Effortless. #### Accessibility Matters Good design is inclusive design. Making your app accessible means building it for everyone, regardless of their physical or cognitive abilities. This isn't just the right thing to do; it dramatically expands your potential audience. Pay attention to the details:
- •Colour Contrast: Is your text easy to read against the background?
- •Font Size: Can users adjust the text size to suit their vision?
- •Screen Reader Compatibility: Have you designed it to work logically for visually impaired users who rely on screen readers?
#### Visual Consistency From the style of your buttons to the hex codes in your colour palette, everything should feel like it belongs together. A consistent visual language reinforces your brand and makes the app feel professional and trustworthy. It also reduces the mental effort for users, because they don't have to relearn how things work every time they open a new screen. This is the kind of polish that separates good apps from great ones.
Forging Your App: The Build and Development Process
This is where the magic happens. All the blueprints, wireframes, and validated ideas finally get turned into a real, functional product. The development process can feel a bit like a black box from the outside, but it's really a structured journey of translating visual designs into the clean, efficient code that will power your app. Most modern teams, ourselves included, swear by an agile methodology. Forget waterfall projects where you wait months for a big reveal. Agile breaks the entire build down into short, manageable cycles called ‘sprints,’ usually lasting one to two weeks. At the end of each sprint, we deliver a small, working piece of the app. This constant cycle of building and reviewing allows for feedback, flexibility, and tangible progress, which is brilliant for avoiding nasty surprises late in the game.
Front-End vs. Back-End: The Two Sides of the Coin
It’s crucial to understand the two core components of any app. The easiest way to think about it is like a restaurant:
- •Front-end development is everything the customer sees and touches, the dining room. It’s the user interface (UI), the buttons you tap, the smooth animations, and the layouts you scroll through. It’s all about creating that polished, responsive, and visually engaging experience on the user's device.
- •Back-end development is the kitchen. This is where the real work happens behind the scenes. It covers the server-side logic, the databases storing user data, and the application programming interfaces (APIs) that make it all run. This is the invisible powerhouse handling user logins, processing payments, and feeding the front-end everything it needs to function.
You can have the most beautiful dining room in the world, but if the kitchen is a mess, nobody gets fed. A great app needs both sides working together flawlessly.
Choosing Your Technology Stack
Picking the right technology stack, the mix of programming languages, frameworks, and tools, is a foundational decision. This choice doesn't just impact the initial build; it dictates your app's long-term performance, scalability, and how easy it is to maintain. A typical modern stack might look something like this:
- •Front-End Framework: We could use React Native for cross-platform apps, or go native with Swift for iOS and Kotlin for Android.
- •Back-End Language:Node.js, Python, or Go are popular choices for their speed and scalability.
- •Database: You've got options like PostgreSQL for structured data or MongoDB when you need more flexibility.
- •Cloud Infrastructure: Services from Amazon Web Services (AWS), Google Cloud, or Microsoft Azure give you the scalable servers and infrastructure to support your app as it grows.
The key is to select technologies that are well-supported, have a strong developer community, and genuinely fit what your project needs to do.
Don’t get mesmerised by the shiniest new technology. A reliable, scalable stack that your development team knows inside and out is always the best choice. Stability and performance trump hype every time.
Integrating APIs and Building Smarter with AI
No app is an island. To add powerful features without building every single thing from scratch, we integrate third-party Application Programming Interfaces (APIs). Think of these as pre-built services that let your app talk to other platforms and borrow their functionality. Some common API integrations we see all the time are:
- •Payment Processing:Stripe or PayPal for secure in-app purchases.
- •Social Logins: Letting users sign up with their Google, Facebook, or Apple accounts.
- •Mapping: The Google Maps API for any location-based features.
- •Messaging: Using a service like Twilio to send SMS notifications or build chat features.
On top of this, artificial intelligence is no longer some far-off concept, it’s a practical tool that helps us build better and faster. AI tools can now generate boilerplate code, suggest optimisations, and even automate parts of the testing process. This frees up our developers to focus their brainpower on crafting the unique, high-value features that will make your app stand out, rather than just reinventing the wheel. Building with these efficiencies from the start means you get a smarter, more robust app in less time.
Testing and Preparing For a Seamless App Launch
Nothing sinks an app faster than a one-star review complaining about bugs, slow performance, or a confusing layout. Before your creation sees the light of day, a rigorous Quality Assurance (QA) process is absolutely non-negotiable. This isn’t just about hunting for crashes; it's about polishing every single interaction until the app is stable, intuitive, and a genuine pleasure to use from the first tap. This is the final hurdle. It’s where you shift focus from building features to perfecting the entire experience. Rushing this stage is a classic false economy, any time you save will be lost tenfold dealing with user churn and scathing feedback. A smooth launch day is the direct result of methodical, comprehensive testing in the weeks leading up to it.

The Three Pillars of Pre-Launch Testing
Your QA strategy needs to be built around three core testing types. Each one scrutinises a different facet of your app’s quality, and together they create a safety net that catches everything from show-stopping bugs to minor user frustrations.
- •Functional Testing: This is the most straightforward part. Does every button, link, and feature do what it's supposed to? Testers will systematically work through every flow, actively trying to break things. This covers everything from form submissions and user logins to in-app purchases and API calls, making sure the app behaves as expected under all sorts of conditions.
- •Usability Testing: This is where you find out if your design actually works for real people. You might have the most functional app in the world, but if users can’t figure out how to navigate it, you've failed. Usability tests involve watching people from your target audience attempt specific tasks. Their feedback is gold, revealing confusing layouts or awkward journeys you’re simply too close to the project to spot yourself.
- •Performance Testing: How does your app hold up when it’s under pressure? Performance testing measures critical metrics like loading times, battery drain, and responsiveness, especially on older devices or with a weak network connection. An app that hogs battery or freezes at a crucial moment gets deleted in a heartbeat. The goal here is a fast, lightweight, and reliable experience for everyone.
Think of QA as the final dress rehearsal. It’s your last chance to find and fix the awkward lines, faulty props, and confusing stage directions before the curtain goes up and your audience arrives.
Navigating the App Store Submission Gauntlet
Once your app is polished and bug-free, it's time to submit it to the Apple App Store and Google Play Store. Don't underestimate this step; it requires careful preparation. Both platforms have notoriously strict guidelines, and getting rejected can cause frustrating delays right when your momentum is building. Getting approved is one challenge; getting noticed is another entirely. This is where optimising your app store listing becomes critical for discovery. Your listing absolutely must include:
- •A Compelling App Name and Icon: Your icon is the first thing anyone sees, make it memorable. Your name should be clear and, if possible, include a relevant keyword.
- •High-Quality Screenshots and Videos: Show, don’t just tell. Use your visuals to highlight the best features and give a real sense of the user experience.
- •A Persuasive Description: Clearly explain what your app does and what problem it solves for the user. Weave in keywords naturally to help your app climb the search rankings.
The UK market is a brilliant example of what local talent can achieve. There are 6,202 British mobile app developers active on Google Play alone, behind 25,229 apps that have an impressive average of 394,870 downloads each. It’s proof that a well-built and well-presented app can make a serious impact. You can discover more insights about the UK app market here. Mastering the submission process can be tricky, as the rules are complex and constantly changing. To sidestep common pitfalls, it’s well worth your time reading up on the best practices for navigating the app store review guidelines to give your launch the smooth, successful start it deserves.
Growing Your App After Launch
Getting your app onto the stores isn't the finish line; it’s the starting gun firing. The real work of building a sustainable, successful app begins the moment it goes live. This is what separates the apps that thrive for years from those that vanish after a few months of fleeting attention. It’s all about shifting your mindset from building to growing. Your focus needs to pivot to a continuous loop of monetisation, analysing user behaviour, and making constant improvements.
Picking a Monetisation Model That Makes Sense
How your app makes money needs to feel like a natural part of the experience, not a clumsy afterthought. An aggressive or confusing monetisation strategy can alienate your hard-won users faster than any bug. The goal is to choose a model that feels fair and, ideally, enhances the value you’re offering. Here are the most common paths you can take:
- •In-App Purchases (IAPs): Perfect for apps offering digital goods or one-off benefits. Think extra lives in a game, a premium filter pack in a photo editor, or unlocking a single advanced feature. It's a straightforward transaction where users pay for specific, tangible value.
- •Subscriptions: This has become the gold standard for content and service-based apps. Users pay a recurring fee (usually monthly or yearly) for ongoing access. It’s the model that powers giants like Spotify and Netflix, and it builds a predictable revenue stream. The catch? You have to consistently deliver fresh value to keep people from cancelling.
- •Advertising: The classic "free-to-use" model. You generate revenue by displaying ads, which works best for apps with high daily traffic, like casual games or news aggregators. The art here is balancing ad frequency and placement so it doesn't completely torpedo the user experience.
- •Freemium: This is a powerful hybrid approach. You offer a core version of the app for free, with certain limitations, then encourage users to upgrade to a paid version for the full suite of features. It’s a fantastic way to let people experience your app’s value firsthand before asking them to open their wallets.
Using Analytics and User Feedback to Guide You
You can't improve what you don't measure. As soon as you launch, your app becomes a rich source of data on real-world user behaviour. Getting tools like Google Analytics for Mobile, Mixpanel, or Firebase set up is non-negotiable. They are essential for tracking key metrics and understanding how people are actually using your product. You’ll want to keep a close eye on a few key performance indicators (KPIs):
- •User Retention Rate: What percentage of users come back to your app after one day, one week, or one month? This is a vital sign of your app's health.
- •Session Length: How long are people spending in the app each time they open it? This is a great indicator of engagement.
- •Daily & Monthly Active Users (DAU/MAU): These raw numbers give you a clear picture of your app's overall user base and whether it's growing or shrinking.
- •Conversion Rate: If you have IAPs or subscriptions, this is the magic number. What percentage of your free users are converting into paying customers?
Data tells you what is happening, but it’s the user feedback that tells you why. You need to combine the quantitative data from analytics with the qualitative feedback from app store reviews, support emails, and social media to get the full picture.
This feedback loop becomes your roadmap for every future update. If users are constantly asking for a certain feature or getting stuck in the same part of the app, that’s your priority list, handed to you on a silver platter. Making your users feel heard is one of the most powerful retention tools you have.
The Never-Ending Job of Maintenance
Finally, remember that an app is a living product. It requires constant care and attention. Neglecting maintenance is a surefire way to watch your app slowly fade into obsolescence as technology moves on without it. Your ongoing work should be a regular cycle of updates. First and foremost, bug fixes are paramount. Every new operating system update or new device model from Apple or Google can introduce unexpected issues. Proactively hunting down and squashing bugs shows your users you're committed to a polished, high-quality experience. Second, performance optimisation is a constant battle. As you add new features, you have to be vigilant about keeping the app fast and responsive. This means managing memory usage and minimising battery drain, two things that users definitely notice. Lastly, staying on top of security vulnerabilities and platform updates isn't just good practice; it's essential. Both Apple and Google regularly update their operating systems and security protocols. Keeping your app compatible not only protects your users' data but is also a mandatory requirement for staying listed on their app stores. This cycle of listening, updating, and maintaining is the engine that drives long-term app success.
Your App Development Questions, Answered
Venturing into the world of app creation can feel a bit daunting. We get it. Over the years, we've heard just about every question you can imagine from businesses and aspiring founders across the UK. Here are our straightforward answers to the ones that come up most often.
How Much Will It Cost to Build My App in the UK?
Honestly, there’s no one-size-fits-all price. The cost for an app in the UK can start from around £20,000 for a lean Minimum Viable Product (MVP) and can easily climb past £150,000 for something with a lot of custom features and complexity. Think of it like building a house. The final cost really boils down to a few key things:
- •The Blueprint (Platform Choice): Are you building for just iPhone, or Android too? Creating separate native apps for both iOS and Android will naturally cost more than using a cross-platform framework that shares code between them.
- •The Interior Design (Complexity): A slick, minimalist design is one thing. Custom animations, beautifully complex user interfaces, and deep, bespoke branding require more time and expertise, which adds to the budget.
- •The Features (Functionality): This is the biggest variable. The more you want your app to do, things like user accounts, payment systems, or connecting with other services through APIs, the more development time it will require.
How Long Does App Development Actually Take?
You can generally expect an app development project to take anywhere from four to nine months. We’ve turned around simpler, more focused apps in as little as three months, but a sophisticated, feature-rich application is more likely to be a six-month-plus journey. That timeline isn’t just coding. It covers everything from the initial discovery and design phases, through development and rigorous testing, all the way to a successful launch. Working with an agile approach, which we're big fans of, means we can often get a working version into your hands for testing much earlier in the process.
Do I Really Need to Know How to Code?
Absolutely not. It's a common myth that you need to be a tech wizard to create a successful app. In fact, many of the best app founders we've worked with are non-technical. Their strength lies in their vision, their understanding of the market, and their business strategy. You’ve got a few great paths forward:
- •Partner with a Studio: This is our bread and butter. Working with an agency like ours gives you a complete, experienced team, designers, developers, project managers, from day one.
- •Assemble a Freelance Team: You can hire individual freelancers to cover different roles. This can work well but requires you to take on the project management yourself.
- •Explore No-Code Platforms: For simpler ideas or building a quick prototype, tools like Bubble or Adalo are fantastic. They let you build apps with visual drag-and-drop editors.
How Do Free Apps Actually Make Money?
It's the million-dollar question, isn't it? Free-to-download apps have several well-trodden paths to profitability. The most common strategies you'll see are in-app advertising (where brands pay to show ads to your users) and in-app purchases (selling digital items, services, or unlocking special features). Another hugely popular route is the freemium model. You offer a solid, free version of the app to get people on board, then provide a paid subscription or one-off purchase to unlock a premium, ad-free, or more powerful version. Ready to stop wondering and start building? Studio Liddell has been crafting high-quality digital experiences since 1996. Our team of seasoned developers and designers is here to guide your project from a spark of an idea to a polished, successful launch. Book a production scoping call with us today