10 Examples of Augmented Reality You Should Know
Augmented reality (AR) has moved far beyond a conceptual gimmick, becoming a practical and powerful tool integrated into everyday applications and specialised industrial workflows. From enhancing how we shop for furniture to revolutionising complex surgical procedures, AR overlays digital information onto the physical world, creating interactive, insightful, and highly valuable user experiences. Understanding its real-world application is key to grasping its strategic potential across various sectors, including retail, entertainment, education, and manufacturing. This article bypasses theoretical discussions and dives straight into a detailed analysis of impactful examples of augmented reality. We will not just list what these applications do; we will dissect the strategic thinking behind them. For each example, we will break down the business objectives, the specific AR technology employed, and the measurable outcomes achieved. You will find actionable takeaways and replicable strategies that you can adapt for your own projects, whether you are developing for enterprise, marketing, or consumer-facing applications. This curated list is designed to provide a strategic blueprint, demonstrating how AR is being used to solve tangible problems, increase user engagement, and drive business growth. By exploring these successful implementations, you will gain a clear understanding of how to move from an AR concept to a high-impact reality.
1. IKEA Place - Furniture Visualization
IKEA Place revolutionised retail by directly addressing a core customer pain point: the uncertainty of how furniture will look and fit in one's own home. This augmented reality application allows users to virtually place true-to-scale 3D models of IKEA products into their living space using just their smartphone. By leveraging Apple's ARKit and Google's ARCore, the app achieves an impressive 98% accuracy in sizing, effectively turning a customer's room into a personal showroom.

This tool is a prime example of augmented reality driving tangible business outcomes by reducing buyer hesitation and minimising product returns.
Strategic Breakdown
- •Objective: Decrease the "imagination gap" for customers, leading to higher purchase confidence and lower return rates. IKEA wanted to make furniture shopping more intuitive and less of a gamble.
- •Technology: The app's success hinges on markerless AR technology (ARKit/ARCore), which uses a device's camera and sensors to understand planes like floors and walls without needing special markers. This makes the experience seamless and accessible.
- •Outcome: IKEA Place has been downloaded millions of times, significantly influencing purchasing decisions and establishing IKEA as an innovator in retail technology.
Actionable Takeaways
For businesses considering similar AR applications, the key is to solve a practical problem. Rather than AR for its own sake, focus on an experience that removes a clear obstacle in the customer journey. Also, ensure the digital assets are of high quality; the realism of the 3D models is critical for user trust. Beyond IKEA Place, there are many other great options for visualising your space. To explore more tools that can help you digitally arrange furniture and decor, consider some of the best interior design apps.
2. Pokémon GO - Location-Based Gaming
Pokémon GO transformed the gaming landscape by fusing a beloved global franchise with location-based augmented reality, encouraging millions to explore the real world. This mobile game overlays virtual creatures, known as Pokémon, onto the physical environment as viewed through a smartphone. Players physically walk around their neighbourhoods to discover, capture, and battle these Pokémon, turning everyday locations into a dynamic, interactive game board. It masterfully combines GPS with AR visualisation to create an immersive experience that promotes outdoor activity and community engagement.

This app stands as one of the most successful examples of augmented reality, demonstrating its power to create shared social experiences and drive real-world behaviour on a massive scale.
Strategic Breakdown
- •Objective: To create a novel gaming experience that leverages a popular IP (Intellectual Property) to get players moving and interacting in the real world, fostering a sense of community and discovery.
- •Technology: The game primarily uses GPS and location services to place Pokémon and points of interest on a real-world map. Its AR functionality (using the phone's camera) overlays the Pokémon onto the player's surroundings during capture sequences, making the experience more immersive.
- •Outcome: With over a billion downloads, Pokémon GO became a cultural phenomenon. It generated immense revenue and sparked global trends, from community-organised events to tourism boards creating sponsored "PokéStops" to attract visitors, proving AR's commercial viability in entertainment.
Actionable Takeaways
The core lesson from Pokémon GO is the power of integrating AR with familiar, real-world activities and established brands. For businesses in entertainment or retail, this means exploring how AR can add a digital layer to physical spaces to drive foot traffic and engagement. Rather than a standalone novelty, AR is most effective when it enhances an existing behaviour, like exploring a city or visiting a shop. Consider how a simple, location-based AR layer could gamify the customer experience or reveal exclusive content.
3. Snapchat Lenses - Social Media AR Filters
Snapchat Lenses transformed social media by integrating interactive augmented reality filters directly into its core user experience. This feature uses sophisticated facial recognition and tracking technology to overlay digital effects, 3D objects, and animations onto a user's face and their surroundings in real-time. By making AR accessible and entertaining for millions of daily users, Snapchat turned a complex technology into a playful, shareable form of self-expression and brand engagement. This application is a powerful example of augmented reality driving viral marketing and user engagement at an unprecedented scale, making AR a mainstream communication tool.
Strategic Breakdown
- •Objective: To increase daily user engagement, create viral marketing opportunities for brands, and differentiate the platform through playful, interactive technology.
- •Technology: Lenses rely heavily on advanced, real-time facial tracking and segmentation algorithms. The launch of Lens Studio democratised AR creation, allowing developers and brands to build and distribute their own experiences on the platform.
- •Outcome: Branded lenses have achieved massive success, such as Taco Bell's Cinco de Mayo filter which garnered over 224 million views in one day. This has established Snapchat as a primary platform for AR-based advertising campaigns.
Actionable Takeaways
For businesses, Snapchat Lenses offer a unique way to connect with a younger demographic through immersive, shareable content. The key is to create an experience that is fun and visually compelling, encouraging organic sharing rather than just a passive ad view. Focus on creating interactive elements, like a mini-game or a surprising transformation, to boost user engagement and shareability. Developing a branded lens can be an effective part of a larger digital marketing strategy.
4. Google Lens - Visual Search and Information
Google Lens transforms the smartphone camera into an intelligent search tool, bridging the gap between the physical world and digital information. This AI-powered augmented reality technology allows users to point their camera at any object, text, or landmark and receive instant, contextually relevant information. It effectively overlays Google's vast knowledge graph onto a user's real-world view, turning curiosity into immediate knowledge and interaction. From translating a menu in real-time to identifying a plant species on a hike, Google Lens is a prime example of augmented reality enhancing daily tasks by making the world around us searchable.
Strategic Breakdown
- •Objective: To integrate Google Search seamlessly into the physical environment, allowing users to "search what they see." The goal is to make information retrieval intuitive and immediate, removing the need to type queries.
- •Technology: The tool relies heavily on computer vision and deep learning. A key technology enabling many AR experiences, especially visual search applications like Google Lens, is sophisticated AI image analysis, which allows devices to 'see' and interpret the physical world. This is combined with Optical Character Recognition (OCR) for text and a massive database for object identification.
- •Outcome: Google Lens is now integrated into millions of Android and iOS devices through the Google App and Google Photos, processing billions of visual searches and solidifying Google's dominance in information access.
Actionable Takeaways
For developers and businesses, Google Lens demonstrates the power of utility-driven AR. The focus should be on creating experiences that provide immediate value or solve a common problem with minimal user effort. Instead of complex new interfaces, leveraging the familiar camera function lowers the barrier to entry. For those looking to learn more about the possibilities, it is worth reading a guide to augmented reality experiences to explore what's achievable.
5. AR Navigation - Google Maps Live View
Google Maps Live View has fundamentally changed how we navigate complex urban environments on foot. This augmented reality feature tackles the common problem of orientating oneself with a 2D map by overlaying digital directions directly onto a live view of the real world. By holding up their phone, users see large arrows, street names, and markers superimposed on their surroundings, making it instantly clear which way to turn or which building to enter. This tool is one of the most practical and widely adopted examples of augmented reality, transforming the abstract task of map-reading into an intuitive, visual experience. It is especially useful for finding precise locations like correct subway exits or specific addresses in dense city centres.
Strategic Breakdown
- •Objective: To eliminate the "last 50 metres" problem in navigation, where users struggle to match their 2D map to their immediate, real-world surroundings. Google aimed to boost user confidence and reduce navigational errors.
- •Technology: Live View combines GPS with a Visual Positioning Service (VPS) that cross-references the device's camera feed with Google's extensive Street View imagery. This allows for hyper-accurate positioning and orientation that GPS alone cannot provide.
- •Outcome: The feature has made urban navigation significantly less stressful for millions of users worldwide, particularly tourists and those in unfamiliar areas. It has solidified Google Maps' position as an essential tool and a leader in practical AR implementation.
Actionable Takeaways
For developers working on location-based services, the key takeaway is the power of combining multiple data sources (GPS, visual data, IMU sensors) to create a robust user experience. Instead of relying on a single technology, a hybrid approach delivers superior accuracy. It is also vital to design the AR interface for quick, glanceable interactions rather than continuous use, ensuring user safety by prompting them to be aware of their surroundings.
6. Medical AR - AccuVein Vein Visualization
AccuVein transforms a critical medical procedure by tackling the common challenge of locating veins for IV insertions and blood draws. This handheld augmented reality device uses non-invasive near-infrared light to detect haemoglobin in a patient's veins. It then projects a real-time, high-definition map of the vasculature directly onto the surface of the skin, making veins that are otherwise invisible to the naked eye clearly visible. This AR tool is a powerful example of augmented reality improving clinical outcomes and patient care. It significantly boosts first-stick success rates, reduces procedure time, and minimises patient discomfort, especially in difficult cases like paediatric or elderly patients.
Strategic Breakdown
- •Objective: To improve the accuracy and efficiency of venous access procedures, thereby enhancing patient safety, reducing healthcare costs associated with multiple attempts, and lowering patient anxiety.
- •Technology: The device leverages near-infrared (NIR) imaging technology combined with a pico-projector. Haemoglobin absorbs the NIR light, creating a contrast that the device's camera captures and projects back onto the skin as a clear vein map.
- •Outcome: Widely adopted in hospitals and clinics, AccuVein has been shown to improve first-stick success by up to 3.5 times. This has established it as an essential tool in fields from emergency medicine to oncology.
Actionable Takeaways
For organisations developing AR for specialised fields, the takeaway is to focus on augmenting, not replacing, professional skill. AccuVein complements a clinician's training by providing crucial data that was previously unavailable. The success lies in integrating seamlessly into an existing workflow to solve a high-stakes problem. To learn more about how AR is being implemented across different medical specialities, you can read more about how augmented reality is transforming healthcare.
7. AR Try-On - Virtual Makeup and Fashion
AR Try-On technology has transformed the beauty and fashion industries by bridging the gap between online browsing and in-person experience. This allows customers to virtually test products like makeup, eyewear, and accessories using their smartphone camera. By employing advanced facial recognition and tracking, these applications accurately overlay digital products onto a user's real-time video feed, showing exactly how an item would look on them without any physical contact.

This innovation is one of the most powerful examples of augmented reality boosting e-commerce sales. Brands like Sephora, L'Oréal, and Warby Parker have pioneered this tech to increase purchase confidence, personalise the shopping journey, and significantly lower product return rates.
Strategic Breakdown
- •Objective: To eliminate the primary barrier to online sales in aesthetic-driven markets: the inability to try before you buy. The goal is to build customer confidence, increase conversion rates, and reduce costly returns.
- •Technology: This relies heavily on sophisticated, markerless facial tracking AR. It uses algorithms to detect key facial features (eyes, lips, nose bridge) and anchor 3D digital products to them with precision, realistically mimicking real-world application.
- •Outcome: Companies using AR try-on have reported substantial increases in engagement and sales. For instance, Perfect Corp’s YouCam Makeup app has over 800 million downloads, demonstrating immense consumer demand for interactive, personalised shopping experiences.
Actionable Takeaways
For retailers, the lesson is to focus AR on personalisation and risk reduction. By giving customers a playful yet practical tool to visualise products on themselves, you remove purchase anxiety. Ensure the digital representations are high-fidelity, as the realism of the colour and texture is crucial for building trust. Explore the different ways you can use augmented reality in marketing to create more engaging customer experiences.
8. AR in Education - Anatomy 4D and Interactive Learning
Augmented reality is fundamentally changing the classroom by transforming abstract concepts into tangible, interactive experiences. Applications like Anatomy 4D allow students to explore complex subjects by overlaying detailed 3D models onto the real world. By simply pointing a device at a printed marker or a textbook, learners can manipulate a virtual human heart, dissect a digital frog, or walk through an ancient ruin, making education far more engaging and effective. This approach caters to diverse learning styles and boosts information retention by turning passive observation into active participation. It's a powerful example of augmented reality making complex knowledge accessible and exciting for a new generation of students.
Strategic Breakdown
- •Objective: To increase student engagement, comprehension, and knowledge retention by making difficult-to-visualise subjects (like biology or chemistry) interactive and three-dimensional.
- •Technology: These applications typically use marker-based AR, where the device’s camera recognises a specific image (a "marker") to trigger and anchor the 3D content. This makes it easy to integrate AR with existing materials like worksheets and textbooks.
- •Outcome: Educational AR tools have been shown to improve student test scores and increase enthusiasm for STEM subjects. They provide a safe, repeatable, and cost-effective alternative to physical dissections or expensive lab equipment.
Actionable Takeaways
For educational institutions or training companies, the key is to apply AR where it adds the most value. Focus on concepts that are hard to grasp in 2D. Start with simple, marker-based experiences before investing in more complex implementations. Ensure AR activities are blended with traditional teaching methods to reinforce learning, and encourage students to collaborate and explore together, turning a solo tech experience into a shared discovery.
9. AR Maintenance and Repair - Industrial Training
Augmented reality is fundamentally transforming industrial sectors by revolutionising equipment maintenance and repair. This technology provides technicians with real-time, hands-free visual guidance overlaid directly onto complex machinery. Using AR headsets like the Microsoft HoloLens or specialised tablets, workers can see step-by-step instructions, digital diagrams, and diagnostic data superimposed on the physical equipment they are servicing. This digital overlay empowers technicians to perform intricate tasks with greater speed and precision. This application is one of the most powerful examples of augmented reality delivering a clear return on investment. It significantly reduces human error, speeds up training for new staff, and minimises costly equipment downtime. Companies like Boeing have famously used AR to cut aircraft wiring production time by 25%, demonstrating its immense operational value.
Strategic Breakdown
- •Objective: To enhance operational efficiency by reducing repair times, minimising errors, and bridging the skills gap. The goal is to empower technicians, improve first-time fix rates, and ensure safety compliance.
- •Technology: These systems rely on marker-based or markerless tracking combined with object recognition to accurately identify machinery and overlay contextual data. SLAM (Simultaneous Localisation and Mapping) technology is crucial for mapping the environment in real time, ensuring digital instructions remain locked to the correct physical components.
- •Outcome: Major industrial players like Siemens, GE, and Porsche have successfully deployed AR maintenance solutions. This has led to quantifiable improvements, including faster service calls, reduced travel costs for expert support, and enhanced knowledge transfer from senior to junior technicians.
Actionable Takeaways
For organisations looking to implement AR for maintenance, begin with a pilot programme targeting a frequent or particularly complex procedure. Success depends on creating instructional content in close collaboration with seasoned technicians to ensure accuracy and practicality. It's also vital to invest in reliable, industrial-grade AR hardware that can withstand challenging work environments. Finally, measure ROI by tracking key metrics like downtime reduction, error rates, and training completion times.
10. AR in Automotive - Head-Up Displays (HUD)
Augmented reality head-up displays (HUDs) are transforming the driving experience by projecting critical information directly onto the windshield. This technology overlays navigation, speed, and safety alerts into the driver's natural line of sight, seamlessly integrating digital data with the real-world view. Advanced systems from manufacturers like Mercedes-Benz and BMW can highlight lane markings or project turn-by-turn arrows onto the actual road ahead, making navigation more intuitive. This implementation is one of the most practical examples of augmented reality, enhancing driver safety by minimising distractions and reducing the cognitive load required to process information. The bar chart below highlights two significant metrics for AR HUDs: their impact on driver focus and their projected market growth.
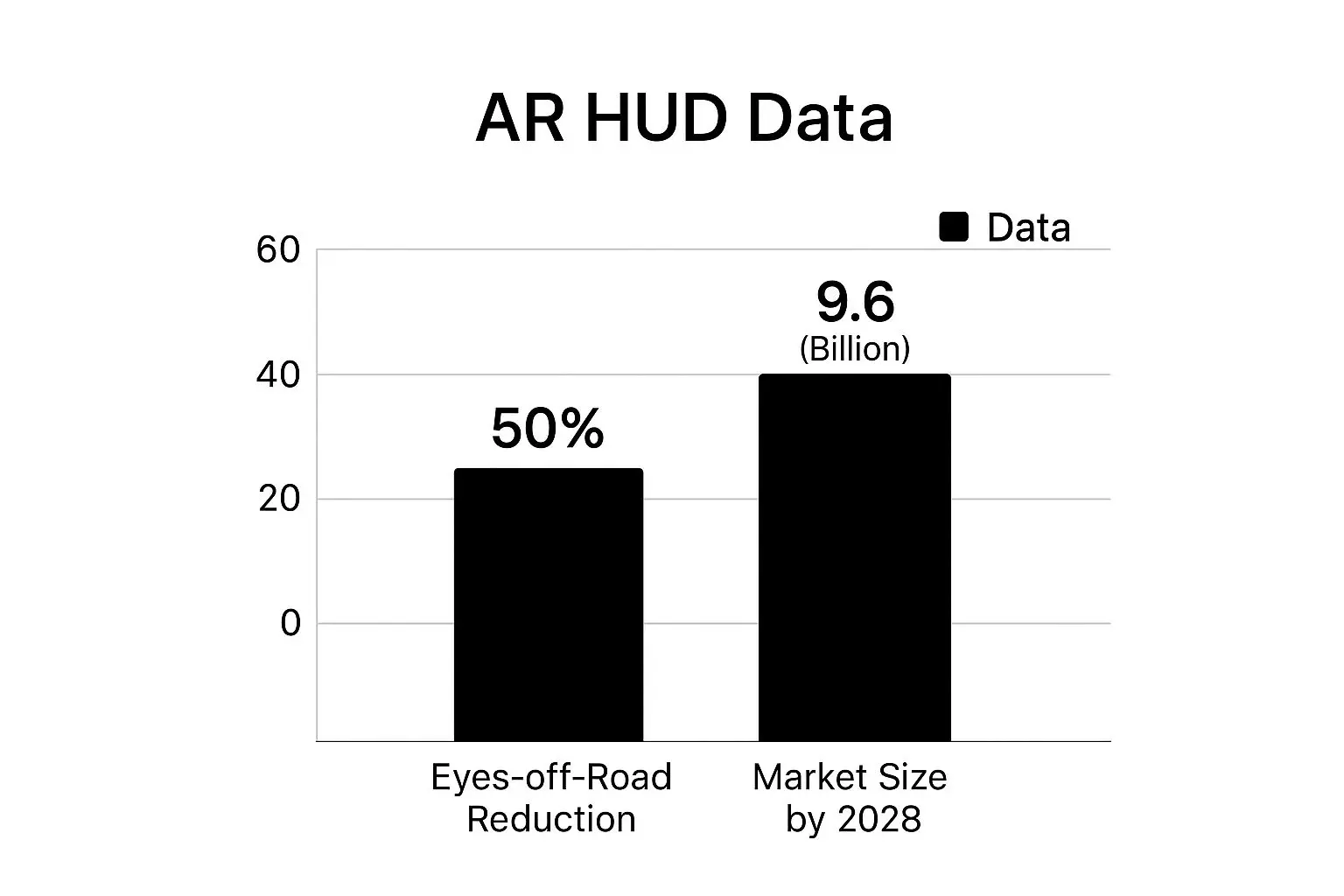
The data clearly illustrates both the immediate safety benefit and the immense commercial potential driving the widespread adoption of this technology.
Strategic Breakdown
- •Objective: To improve road safety by reducing "eyes-off-road" time and enhancing situational awareness. The goal is to provide essential data without forcing drivers to look down at a dashboard or console.
- •Technology: These systems use a combination of projectors, combiners, and sophisticated sensors (GPS, cameras, gyroscopes) to create a virtual image that appears to float over the road. The technology must accurately track the car's position and the driver's perspective in real-time.
- •Outcome: Major automotive brands like Audi and Hyundai have integrated AR HUDs as key features in their premium models, establishing a new standard for in-car interfaces. This has led to a significant reduction in driver distraction and is a major selling point for new vehicles.
Actionable Takeaways
For developers in the automotive or tech space, the key is focusing on contextual relevance. The AR information must be timely, non-intrusive, and directly related to the immediate driving task. Businesses should also prioritise a seamless user experience; ensure the display is clear in all lighting conditions and easy to customise. For drivers, remember to clean your windshield regularly for optimal display clarity and take time to familiarise yourself with the system in a safe environment before relying on it fully.
Top 10 Augmented Reality Examples Comparison
| Feature/Aspect | IKEA Place - Furniture Visualization | Pokémon GO - Location-Based Gaming | Snapchat Lenses - Social Media AR Filters | Google Lens - Visual Search and Information | AR Navigation - Google Maps Live View | Medical AR - AccuVein Vein Visualization | AR Try-On - Virtual Makeup and Fashion | AR in Education - Anatomy 4D and Interactive Learning | AR Maintenance and Repair - Industrial Training | AR in Automotive - Head-Up Displays (HUD) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Implementation Complexity 🔄 | Moderate, requires ARKit/ARCore integration | High, combines GPS, AR, social features | Moderate, facial recognition & real-time effects | Moderate, uses AI, ML, computer vision | High, GPS + VPS + Street View + AR integration | High, specialized medical device & imaging tech | Moderate, facial tracking & 3D rendering | Moderate to high, 3D models & interaction layers | High, AR glasses/tablets + IoT + remote collaboration | High, real-time projection & vehicle integration |
| Resource Requirements ⚡ | Smartphone with AR hardware, moderate processing | Smartphone with GPS, constant internet, battery | Modern front camera, app processing power | Smartphone camera, internet connection | Smartphone GPS, camera, data connectivity | Specialized handheld device, staff training | Smartphone or smart mirrors, quality camera needed | Devices for students or groups, software licenses | AR HMDs/tablets, connectivity, training | Vehicle HUD hardware, software, sensors |
| Expected Outcomes 📊 | Accurate furniture visualization, reduces returns | Enhanced outdoor game engagement, social bonding | Fun, viral user engagement, brand marketing | Instant object recognition and information retrieval | Intuitive walking navigation, reduced confusion | Improved vein access success, reduced patient discomfort | Increased purchase confidence, lower product returns | Improved learning retention and engagement | Reduced downtime, improved training and safety | Enhanced driver safety, situational awareness |
| Ideal Use Cases 💡 | Home furnishing decisions | Location-based mobile gaming & community events | Social media interaction and marketing campaigns | Visual search, education, shopping assistance | Pedestrian navigation in urban/unfamiliar areas | Medical procedures needing vein visualization | Beauty/fashion virtual try-on online and in-store | STEM education, interactive learning | Industrial maintenance, remote expert support | Driving assistance and navigation |
| Key Advantages ⭐ | True-to-scale 3D models, cross-platform, easy comparison | Physical activity encouragement, social connectivity | Wide reach, ease of use, content creation democratization | Versatile AI-powered recognition, Google ecosystem | Clear directional AR, reduces map confusion | Non-invasive, increases first-stick success | Hygienic, 24/7 accessibility, personalized recommendations | Enables complex topic visualization | Reduces errors and downtime, expert support | Keeps driver’s eyes on the road, reduces cognitive load |
Final Thoughts
As we've journeyed through these diverse examples of augmented reality, a clear and compelling narrative emerges. AR is no longer a futuristic novelty confined to science fiction; it is a powerful, practical tool actively reshaping industries, enhancing user experiences, and creating tangible value today. From the intuitive functionality of IKEA Place transforming retail, to the life-saving precision of AccuVein in healthcare, the applications are as varied as they are impactful. The key thread connecting these successful implementations is not the technology itself, but the strategic thinking behind it. Each example demonstrates a deep understanding of a specific user need or business problem. Pokémon GO didn't just overlay digital creatures onto the real world; it tapped into a universal desire for discovery and community. Similarly, industrial AR for maintenance isn't about flashy visuals; it's about delivering critical information directly into a technician's line of sight, minimising errors and maximising efficiency.
Core Takeaways for Your AR Strategy
Reflecting on the case studies, several core principles stand out for any organisation looking to leverage AR:
- •Context is King: The most successful AR experiences are seamlessly integrated into the user's environment and task. Google Maps' Live View works because it solves the immediate, real-world problem of navigating a complex urban junction on foot.
- •Utility Over Novelty: While the 'wow' factor is an initial draw, long-term engagement is driven by genuine utility. Virtual try-on features persist because they solve a real-world friction point in e-commerce, reducing returns and increasing purchase confidence.
- •Focus on the User Journey: Effective AR isn't an isolated feature. It's a touchpoint within a larger customer journey. Consider how AR can bridge the gap between digital discovery and physical interaction, as seen in retail and exhibition applications.
The Path Forward with Augmented Reality
The examples of augmented reality explored in this article are merely the beginning. As hardware becomes more accessible-from ubiquitous smartphones to sophisticated headsets-and development platforms like Unity and Unreal become more powerful, the barrier to entry is lowering. The opportunity now lies in creative, strategic application. Businesses, educators, and creators who focus on solving real problems and delivering intuitive, value-driven experiences will lead the next wave of spatial computing innovation. The challenge is to move beyond simply asking "what can we do with AR?" and instead ask "what user problem can we uniquely solve with AR?" Answering that question is the first step towards building the next great AR success story. Ready to move from inspiration to implementation? The team at Studio Liddell has been at the forefront of crafting immersive AR and VR experiences for exhibitions, training, and brand engagement since 1996. We can help you develop a strategic AR concept that delivers real impact, from initial concept sprints to full-scale deployment. Book a discovery workshop with our team to explore your AR potential.